
When it comes to power supplies, understanding the nuances between linear, switching, digital, and programmable types is crucial for making an informed decision.
Differences:
Working Principles
Linear Power Supply: It controls the output voltage by adjusting the conduction degree of the power transistor to stabilize the output voltage. The power transistor operates in the linear amplification region, similar to a variable resistor, and adjusts the output voltage by changing its resistance value.
Switching Power Supply: It uses the conduction and cut-off of the power switch tube to control the conversion of electrical energy. It adjusts the output voltage by changing the ratio (duty cycle) of the conduction time of the switch tube to the cycle. The switch tube works in the switching state, that is, conduction or cut-off, which greatly reduces the power loss.
Digital Control Power Supply: With digital signal processing as the core, it controls the output of the power supply through digital circuits and algorithms. It converts the input analog signal into a digital signal, and after digital processing, it is converted back into an analog control signal to adjust the output voltage or current of the power supply.
Programmable Control Power Supply: It usually refers to controlling the output of the power supply through computer programming or other external control signals. It can receive instructions from devices such as computers and controllers, and adjust output parameters such as output voltage and current according to preset programs or parameters.
Performance Characteristics
Linear Power Supply: The advantages are high output voltage stability, small ripple coefficient, and low electromagnetic interference (EMI), making it suitable for circuits with high requirements for power supply stability. The disadvantage is relatively low efficiency, especially in the case of high voltage and large current output, the power loss is relatively large, and the volume and weight are also relatively large.
Switching Power Supply: The advantages are high efficiency, generally up to more than 80% - 90%, small volume, light weight, and the ability to adapt to a wide input voltage range. The disadvantage is that the output ripple is relatively large, the EMI is strong, and good filtering and shielding measures are required. Our power supply comes with low ripple, and 30v 10a less than 80mV.
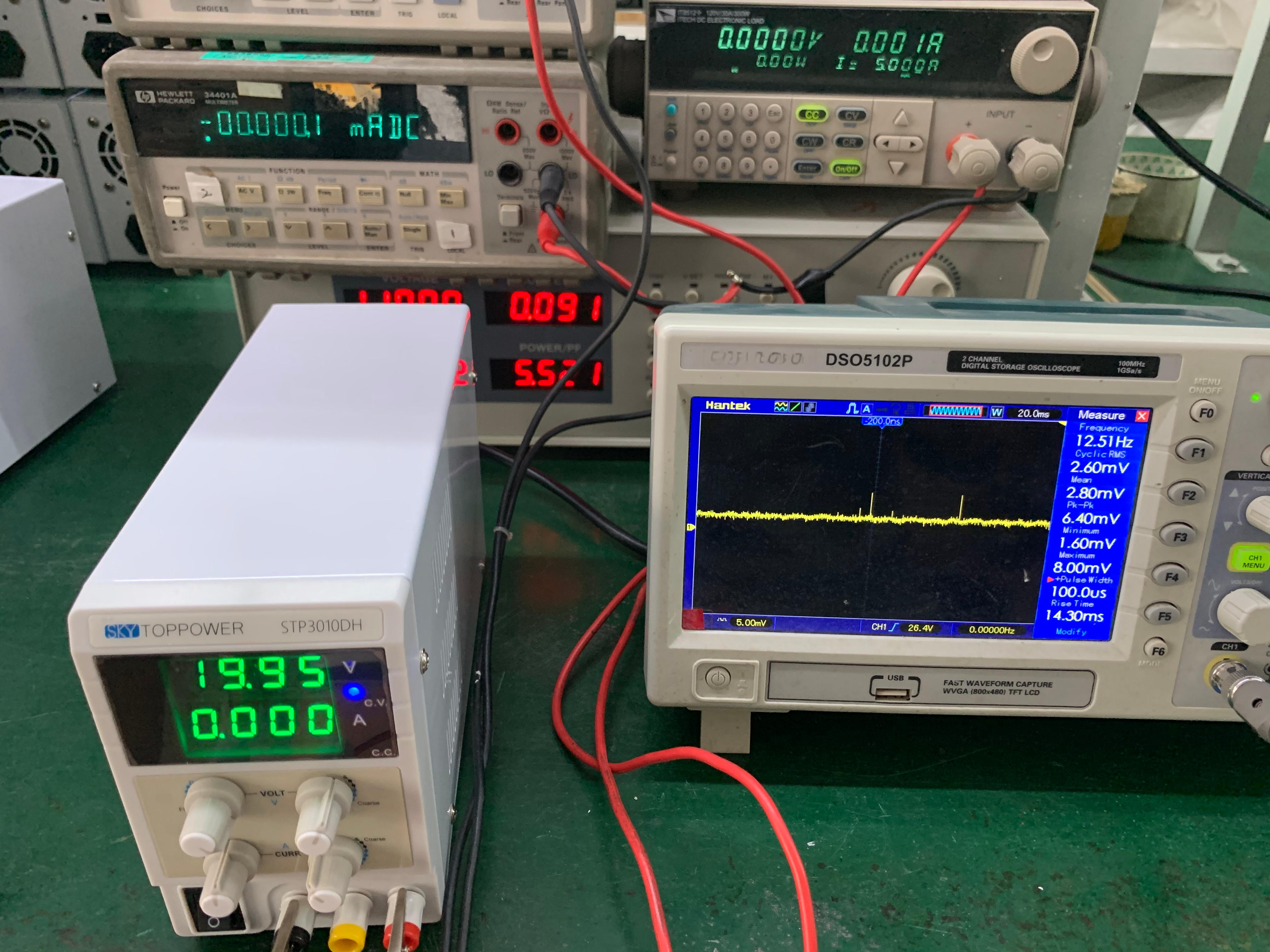
Digital Control Power Supply: It has high precision and flexibility. Various complex control algorithms and functions can be realized through software programming, such as multiple output modes, overvoltage and overcurrent protection, etc. Its precision and stability are usually better than traditional analog power supplies.
Programmable Control Power Supply: It can be conveniently integrated with computers or other control systems to achieve remote control and automated testing. Users can accurately control the output parameters of the power supply by writing programs, improving test efficiency and accuracy.
Application Scenarios
Linear Power Supply: It is often used in occasions with extremely high requirements for power supply quality, such as audio amplifiers, precision instruments, and analog circuits. These devices have strict requirements for the ripple and stability of the power supply to ensure their normal operation and high-precision performance.
Switching Power Supply: It is widely used in various electronic devices, such as computer power supplies, mobile phone chargers, industrial automation equipment, communication equipment, etc. These devices have high requirements for the efficiency and volume of the power supply and can meet the power supply needs of different devices.
Digital Control Power Supply: It is mostly applied in scientific research, laboratories, electronic equipment research and development and other fields. It can provide accurate adjustable power supplies, facilitating researchers to conduct various experiments and tests and meeting the precise requirements for power supply parameters in different experiments.
Programmable Control Power Supply: It is often used in automated testing systems, semiconductor manufacturing equipment, aerospace and other fields. Through computer programming, remote control and precise adjustment of the power supply can be realized, improving production efficiency and testing accuracy, and it is also convenient for realizing large-scale automated production and testing.
Selection
According to Application Requirements: If it is an analog circuit or precision instrument with extremely high requirements for power supply stability and ripple, a linear power supply is a better choice; for general electronic devices such as computers and mobile phones, a switching power supply usually can meet the requirements; if precise parameter adjustment and control are required, such as the power supply in a laboratory, a digital control power supply or a programmable control power supply is more appropriate.
Consider Efficiency and Power: For high-power applications, the high efficiency of the switching power supply can reduce energy consumption and heat dissipation problems, which is the preferred choice; for low-power applications with low requirements for efficiency, the simplicity and stability of the linear power supply may have more advantages.
Pay Attention to Cost and Volume: Due to its high efficiency and high integration degree, the switching power supply has a relatively low cost during mass production and a small volume; the linear power supply has a relatively high cost and a large volume. If you are sensitive to cost and volume, you should give priority to the switching power supply. Digital control power supplies and programmable control power supplies usually have a higher price, but they have powerful functions and are suitable for occasions with demanding performance requirements and an allowable budget.
Combine with the Usage Environment: In complex electromagnetic environments, power supplies with good electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) need to be selected. Switching power supplies require additional EMC measures; while linear power supplies have lower EMI and are more suitable for use in environments sensitive to electromagnetic interference.
Contact: MDLtool
Phone: +86-16675407880
Tel: +86-16675407880
Email: info@mdltool.com
Add: 3F,Building A2,Baicai Industrial Park,19 Tianbao Road,Baoan,Shenzhen GD ,PRC 518100